biocmask Usage Guide
Justin Landis
Michael Love
10/10/2024
Source:vignettes/biocmask.Rmd
biocmask.RmdQuick start
biocmask provides efficient abstractions to the
SummarizedExperiment such that using common dplyr functions
feels as natural to operating on a data.frame or
tibble. biocmask uses data-masking
from the rlang package in order to connect dplyr functions
to SummarizedExperiment slots in a manner that aims to be
intuitive and avoiding ambiguity in outcomes.
Supported data types and operations
biocmask works on SummarizedExperiment objects,
as well as most classes derived from this, including
DESeqDataSet, SingleCellExperiment, etc.
It supports the following operations:
mutateselectsummarizepullfilterarrange
Typical use case
library(biocmask)
# add data (mutate) to any of the three tables,
# assay, colData, rowData,
# ...using contextual helpers cols() and rows()
airway |>
mutate(log_counts = log1p(counts),
cols(treated = dex == "trt"),
rows(new_id = paste0("gene-", gene_name)))## class: RangedSummarizedExperiment
## dim: 63677 8
## metadata(1): ''
## assays(2): counts log_counts
## rownames(63677): ENSG00000000003 ENSG00000000005 ... ENSG00000273492
## ENSG00000273493
## rowData names(4): gene_id gene_name gene_biotype new_id
## colnames(8): SRR1039508 SRR1039509 ... SRR1039520 SRR1039521
## colData names(5): SampleName cell dex albut treatedThe operations can span contexts, and only the necessary data will be extracted from each context for computation:
airway$sizeFactor <- runif(8, .9, 1.1)
# making scaled counts, then computing row means:
airway |>
mutate(scaled_counts = counts / .cols$sizeFactor, #
rows(ave_scl_cts = rowMeans(.assays_asis$scaled_counts)))## class: RangedSummarizedExperiment
## dim: 63677 8
## metadata(1): ''
## assays(2): counts scaled_counts
## rownames(63677): ENSG00000000003 ENSG00000000005 ... ENSG00000273492
## ENSG00000273493
## rowData names(4): gene_id gene_name gene_biotype ave_scl_cts
## colnames(8): SRR1039508 SRR1039509 ... SRR1039520 SRR1039521
## colData names(5): SampleName cell dex albut sizeFactorCalling .cols in the assay context produces an object of
the matching size and orientation to the other assay data.
Alternatively we could have used purrr to compute row means:
airway |>
mutate(scaled_counts = counts / .cols$sizeFactor,
# You may expect a list when accessing other contexts
# from either the rows() or cols() contexts.
rows(ave_scl_cts = purrr::map_dbl(.assays$scaled_counts, mean)))## class: RangedSummarizedExperiment
## dim: 63677 8
## metadata(1): ''
## assays(2): counts scaled_counts
## rownames(63677): ENSG00000000003 ENSG00000000005 ... ENSG00000273492
## ENSG00000273493
## rowData names(4): gene_id gene_name gene_biotype ave_scl_cts
## colnames(8): SRR1039508 SRR1039509 ... SRR1039520 SRR1039521
## colData names(5): SampleName cell dex albut sizeFactorSee below for details on how objects are made available across contexts.
biocmask also enables common grouping and summarization
routines:
summary <- airway |>
group_by(rows(gene_biotype)) |>
summarize(col_sums = colSums(counts),
# may rename rows with .features
rows(.features = unique(gene_biotype)))
# summarize returns a SummarizedExperiment here,
# retaining rowData and colData
summary |> rowData()## DataFrame with 30 rows and 1 column
## gene_biotype
## <character>
## protein_coding protein_coding
## pseudogene pseudogene
## processed_transcript processed_transcript
## antisense antisense
## lincRNA lincRNA
## ... ...
## IG_C_pseudogene IG_C_pseudogene
## TR_D_gene TR_D_gene
## IG_J_pseudogene IG_J_pseudogene
## 3prime_overlapping_ncrna 3prime_overlapping_n..
## processed_pseudogene processed_pseudogene
# visualizing the output as a tibble:
library(tibble)
summary |>
pull(col_sums) |>
as_tibble(rownames = "type")## # A tibble: 30 × 9
## type SRR1039508 SRR1039509 SRR1039512 SRR1039513 SRR1039516 SRR1039517
## <chr> <dbl> <dbl> <dbl> <dbl> <dbl> <dbl>
## 1 protein_co… 19413626 45654 4 1188 96378 0
## 2 pseudogene 17741060 45864 4 462 38656 0
## 3 processed_… 23926011 133335 0 1049 64884 0
## 4 antisense 14360299 120060 4 1113 36267 0
## 5 lincRNA 23003444 206075 6038 626 81606 0
## 6 polymorphi… 29233398 125015 5618 803 88868 0
## 7 IG_V_pseud… 18114369 145078 7662 316 44385 0
## 8 IG_V_gene 20103401 170641 5579 256 92499 0
## 9 sense_over… 807285 147563 7869 339 491 0
## 10 sense_intr… 733916 149486 9443 202 502 0
## # ℹ 20 more rows
## # ℹ 2 more variables: SRR1039520 <dbl>, SRR1039521 <dbl>Related work
We note that biocmask is highly related to other
tidyomics projects including:
- tidySummarizedExperiment
- plyranges
- DFplyr
- and more.
Here we have focused on the design principles of function endomorphism (returning the same object that was input), avoiding ambiguity through strictly defined behavior (potentially at the expense of longer code), and allowing the user the convenience of multiple expressions for the same result, some of which may have improved computational performance.
A Note on tidySummarizedExperiment
At the moment, biocmask and
tidySummarizedExperiment export conflicting functions as
they both define dplyr methods for manipulating the
SummarizedExperiment class. biocmask exists as
an alternative to tidySummarizedExperiment and enables a
unique approach to working with the SummarizedExperiment
class. We advise limiting your analysis to one package or another, as
which methods that are available in your search path depends on the
order in which the packages are attached leading to unexpected
behaviors.
Manipulating SummarizedExperiment with
biocmask
The SummarizedExperiment object contains three main
components/“contexts” that we mask, the assays(),
rowData()1 and colData().
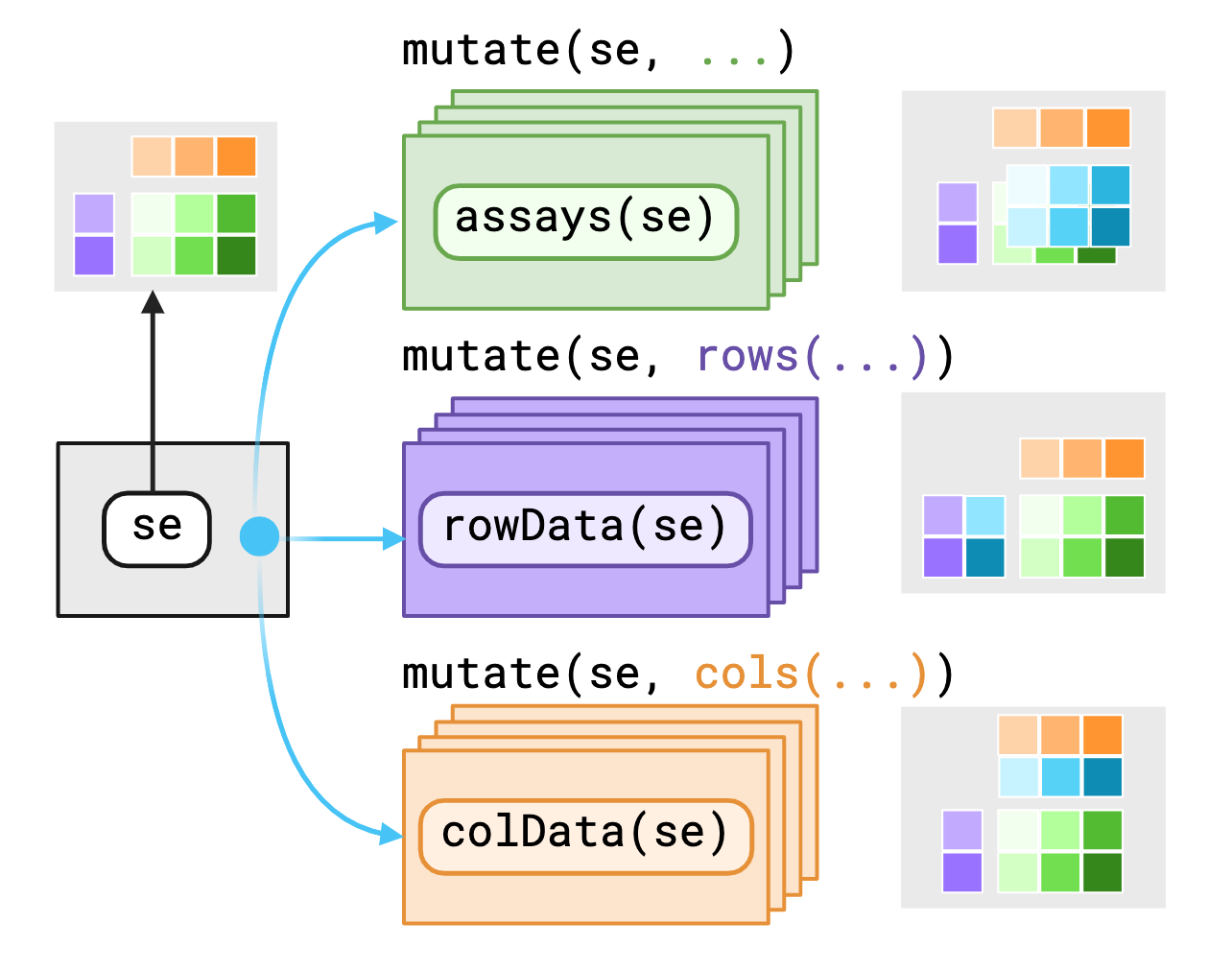
biocmask provides variables as-is to data within
their current contexts enabling you to call S4 methods on S4
objects with dplyr verbs. If you require access to
variables outside the context, you may use pronouns made
available through biocmask to specify where to find those
variables.
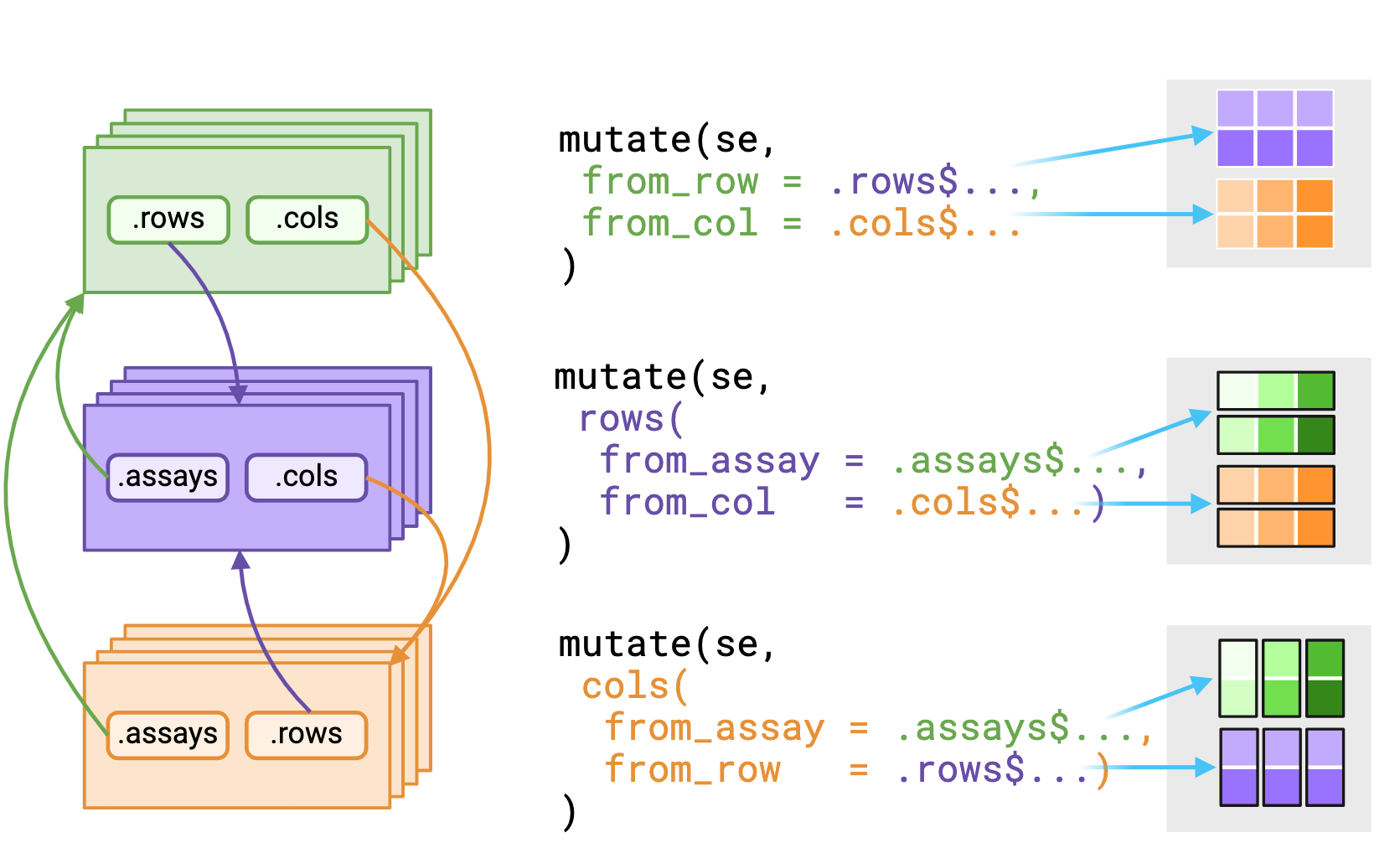
_asis variant that returns underlying data
without reshaping it to fit the context. Figure made with Biorender
The .assays, .rows and .cols
pronouns outputs depends on the evaluating context. Users should expect
that the underlying data returned from .rows or
.cols pronouns in the assays
context is a vector, replicated to match size of the assay
context.
Alternatively, using a pronoun in either the rows() or
cols() contexts will return a list equal in length to
either nrows(rowData()) or nrows(colData())
respectively.
assay context
- Default evaluation context
-
.assayscontextual pronoun, returns list of the matrix, sliced by the dimension it was referenced from.- within the rowData context:
.assays$foois an alias forlapply(seq_len(nrow()), \(i, x) x[i,,drop=FALSE], x = foo) - within the colData context:
.assays$foois an alias forlapply(seq_len(ncol()), \(i, x) x[,i,drop=FALSE], x = foo)
- within the rowData context:
-
.assays_asispronoun to direct bindings inassays() -
assay_ctx(expr, asis = FALSE)short hand to bind the assay context in front of the current context.
rows context
-
rows(...)sentinel function call to indicate evaluation context. -
.rowscontextual pronoun- within assay context:
.rows$foois an alias forvctrs::vec_rep(foo, times = ncol()) - within colData context:
.rows$foois an alias forvctrs::vec_rep(list(foo), times = n())
- within assay context:
-
.rows_asispronoun to direct bindings inrowData() -
row_ctx(expr, asis = FALSE)shorthand to bind the rowData context in front of the current context
cols context
-
cols(...)sentinel function call to indicate evaluation context. -
.colscontextual pronoun- within assay context:
.cols$foois an alias forvctrs::vec_rep_each(foo, times = nrow()) - within rowData context:
.rows$foois an alias forvctrs::vec_rep(list(foo), times = n())
- within assay context:
-
.cols_asispronoun to direct bindings incolData() -
col_ctx(expr, asis = FALSE)shorthand to bind the colData context in front of the current context
Multiple expressions enabled via biocmask
We can compare two ways of dividing out a vector from
colData along the columns of assay data:
# here the `.cols$` pronoun reshapes the data to fit the `assays` context
airway |>
mutate(scaled_counts = counts / .cols$sizeFactor)## class: RangedSummarizedExperiment
## dim: 63677 8
## metadata(1): ''
## assays(2): counts scaled_counts
## rownames(63677): ENSG00000000003 ENSG00000000005 ... ENSG00000273492
## ENSG00000273493
## rowData names(3): gene_id gene_name gene_biotype
## colnames(8): SRR1039508 SRR1039509 ... SRR1039520 SRR1039521
## colData names(5): SampleName cell dex albut sizeFactor
# this is equivalent to the following, where we have to transpose
# the `counts` assay data twice to enable the correct recycling
# of the size factor vector
airway |>
mutate(scaled_counts = t(t(counts) / .cols_asis$sizeFactor))## class: RangedSummarizedExperiment
## dim: 63677 8
## metadata(1): ''
## assays(2): counts scaled_counts
## rownames(63677): ENSG00000000003 ENSG00000000005 ... ENSG00000273492
## ENSG00000273493
## rowData names(3): gene_id gene_name gene_biotype
## colnames(8): SRR1039508 SRR1039509 ... SRR1039520 SRR1039521
## colData names(5): SampleName cell dex albut sizeFactorAdvanced features
Object integrity
biocmask provides an opinionated framework for how
dplyr verbs should interact with
SummarizedExperiment objects. In general,
biocmask will not allow any operations that it could not
guarantee a valid return object.
It is for this reason that arrange(),
filter() and group_by() do not allow
operations in the default assay context, as this would likely break the
assumed structure of a SummarizedExperiment object.
group_by()
biocmask also supports group_by operations
allowing users to query information with dplyr::n() or
dplyr::cur_group_id(). However due to the linked structure
of a SummarizedExperiment object and biocmask
providing multiple evaluation contexts, grouping operations would be
complex and return values would be potentionally ambiguous.
It is for this reason that groupings are themselves contextual. The assay context is dependently linked to both the groupings of the rows and cols contexts but, the grouping of rows is ignored when viewed from the cols context and similarly the grouping of cols is ignored when viewed from the rows context. In this way, we have chosen to make the groupings of rows and cols independent between each other. The below figure attempts to show how groupings are conditionally dropped for the scope of an evaluation.
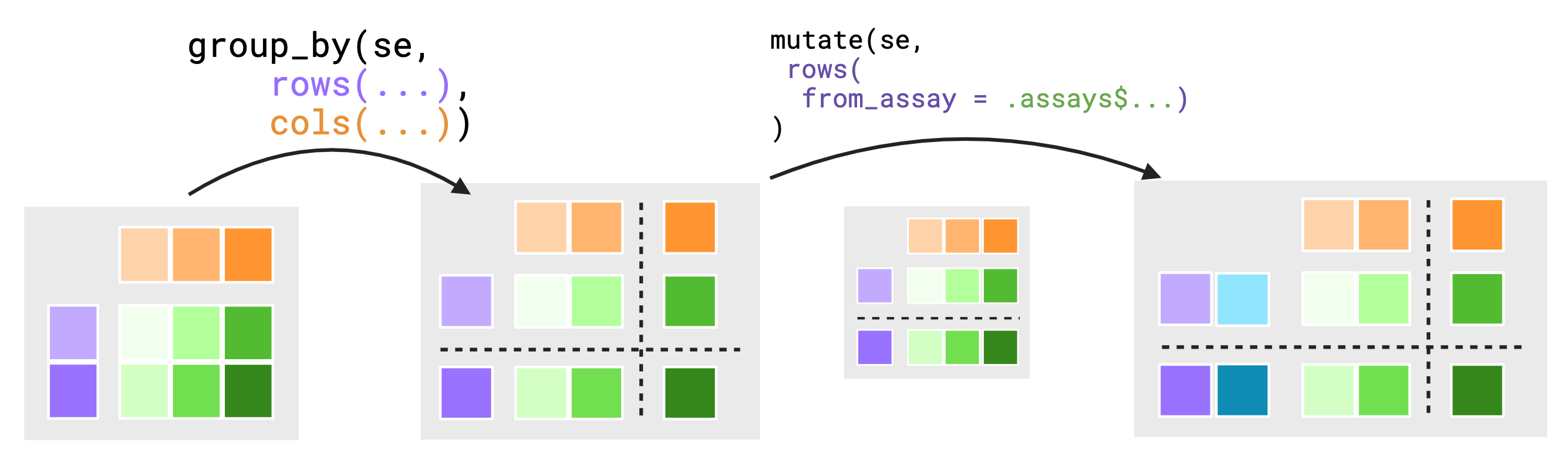
To further motivate this choice, suppose we did not drop grouping
values. Assume you have a small 5 by 4 SummarizedExperiment
object. Both of the rowData() and colData()
are grouped such that there are 2 groups in both rowData()
and colData() totaling in 4 groups across the assays.
group_by(se_simple, rows(direction), cols(condition)) |>
mutate(rows(data_from_cols = .cols$condition))The above syntax implies we wish to move data from the
colData() into the rowData(). From a
previously established conventions, we would expect the output to be an
alias for
vctrs::vec_rep(list(condition), times = n()).
Additionally the rows() sentinal will expect that the
output of .cols$condition will need to match the size of
the evaluation context.
Unfortunately, this becomes extremely difficult to resolve with the
current conventions. Without dropping the cols() groupings,
each rows() grouping is evaluated equal to the number of
groups in cols(). At first glance, this may seem desirable,
but the problem arises when considering how theses outputs across groups
should be stored per group of rows(). For example, should
the output of the .cols$condition return a list equal to
the number of groups of the column context? If yes, we would need to
consider the size stability of the output context! Assuming that
rowData() has at least one group with three elements, there
is no guarentee it would fit (this also makes a poor assumption that the
elements of rowData() somehow correspond to the groups of
colData()). Thus we would be left with wrapping all the
results in a list and replicating to the appropriate size. When its all
said and done, we would have a list of lists, which is difficult to
reason about, potentionally unexpected and painful to work with. For
this reason the only groupings present in the rowData()
context are the groupings in rowData(), and similarly for
the colData() context.
Printing
Motivated by the show/print function in
tidySummarizedExperiment, we visualize the data as if it was
tabular. biocmask offers the option to opt-in on this
behavior by setting the associated global option:
options("show_SummarizedExperiment_as_tibble_abstraction" = TRUE)Alternatively, you may use helper functions
use_show_tidy() and use_show_default() to
enable and disable this alternative printing respectively.
Since biocmask aims to leave the input data as-is when
possible, we have considered providing support for printing
S4Vectors within a tibble(). To be clear,
biocmask will not allow you to put
S4Vectors inside a tibble(), but will allow
for S4Vectors to be printed with pillar(), the
formatting engine behind tibble() pretty printing.
To enable this behavior, before any data is reported to the user, we
proxy any S4Vector with a custom vctrs_vctr
object with biocmask::vec_phantom(). In truth, the
vec_phantom object is a simple integer vector with a
“phantomData” attribute. This allows us to carry along
S4Vector through pillar()’s printing pipeline
until it is time to print the column.
The pillar_shaft() method for vec_phantom
will format the S4 data with biocmask_pillar_format()
generic, which by default calls S4Vectors::showAsCell().
Users are free to create their own methods for S4 vectors that differ
from S4Vectors::showAsCell() if they like, as seen in
?`biocmask-printing`
renaming rows or columns
Inspired by tidySummarizedExperiment,
biocmask provides access to the rownames and colnames of a
SummarizedExperiment object by installing
.features and .samples into the
rowData() and colData() contexts respectively.
These are special in that assigning a value to .features in
the rowData() context or .samples in the
colData() context does not create a new column, but changes
the rownames or colnames of the resulting object.
se_simple## class: SummarizedExperiment
## dim: 5 4
## metadata(0):
## assays(2): counts logcounts
## rownames(5): row_1 row_2 row_3 row_4 row_5
## rowData names(3): gene length direction
## colnames(4): col_1 col_2 col_3 col_4
## colData names(2): sample condition
# moving data to rownames and colnames
se_simple |>
mutate(
orig_names = sprintf(
"%s-%s",
# .features is installed in the rows() context
.rows$.features,
# .samples is installed in the cols() context
.cols$.samples),
rows(.features = gene,
# deleting rowData column
gene = NULL),
cols(.samples = sample,
# deleting colData column
sample = NULL)
)## class: SummarizedExperiment
## dim: 5 4
## metadata(0):
## assays(3): counts logcounts orig_names
## rownames(5): g1 g2 g3 g4 g5
## rowData names(2): length direction
## colnames(4): s1 s2 s3 s4
## colData names(1): conditionTroubleshooting and best practices
while biocmask takes inspiration from the data masks
used in dplyr, they are unfortunately more complex. This
means there is some overhead in creating the evaluation mask per dplyr
verb. Try to reduce the number of dplyr verb calls and
instead increase the content of each verb. For example instead of
doing:
do the following
.data |>
mutate(
foo = bar,
baz = foo^2
)Community and support
Please feel free to post questions about biocmask
to:
- the Bioconductor support site
- as an Issue on GitHub
- in the
#tidiness_in_biocchannel on the community-bioc Slack
For code contributions:
- For small fixes, feel free to post a PR on GitHub
- For larger structural changes to the package code, please reach out to the development team first through one of the above channels.
Thanks for your interest in biocmask!
Session info
devtools::session_info()## ─ Session info ───────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────
## setting value
## version R version 4.4.1 (2024-06-14)
## os Ubuntu 22.04.4 LTS
## system x86_64, linux-gnu
## ui X11
## language en
## collate en_US.UTF-8
## ctype en_US.UTF-8
## tz UTC
## date 2024-10-10
## pandoc 3.2 @ /usr/bin/ (via rmarkdown)
##
## ─ Packages ───────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────
## package * version date (UTC) lib source
## abind 1.4-8 2024-09-12 [1] RSPM (R 4.4.0)
## airway * 1.24.0 2024-05-02 [1] Bioconductor 3.19 (R 4.4.1)
## Biobase * 2.64.0 2024-04-30 [1] Bioconductor 3.19 (R 4.4.1)
## BiocGenerics * 0.50.0 2024-04-30 [1] Bioconductor 3.19 (R 4.4.1)
## biocmask * 0.99.18 2024-10-10 [1] Bioconductor
## bslib 0.8.0 2024-07-29 [2] RSPM (R 4.4.0)
## cachem 1.1.0 2024-05-16 [2] RSPM (R 4.4.0)
## cli 3.6.3 2024-06-21 [2] RSPM (R 4.4.0)
## crayon 1.5.3 2024-06-20 [2] RSPM (R 4.4.0)
## DelayedArray 0.30.1 2024-05-07 [1] Bioconductor 3.19 (R 4.4.1)
## desc 1.4.3 2023-12-10 [2] RSPM (R 4.4.0)
## devtools 2.4.5 2022-10-11 [2] RSPM (R 4.4.0)
## digest 0.6.37 2024-08-19 [2] RSPM (R 4.4.0)
## dplyr * 1.1.4 2023-11-17 [1] RSPM (R 4.4.0)
## ellipsis 0.3.2 2021-04-29 [2] RSPM (R 4.4.0)
## evaluate 1.0.0 2024-09-17 [2] RSPM (R 4.4.0)
## fansi 1.0.6 2023-12-08 [2] RSPM (R 4.4.0)
## fastmap 1.2.0 2024-05-15 [2] RSPM (R 4.4.0)
## fs 1.6.4 2024-04-25 [2] RSPM (R 4.4.0)
## generics 0.1.3 2022-07-05 [1] RSPM (R 4.4.0)
## GenomeInfoDb * 1.40.1 2024-05-24 [1] Bioconductor 3.19 (R 4.4.1)
## GenomeInfoDbData 1.2.12 2024-06-25 [1] Bioconductor
## GenomicRanges * 1.56.1 2024-06-12 [1] Bioconductor 3.19 (R 4.4.1)
## glue 1.8.0 2024-09-30 [2] RSPM (R 4.4.0)
## highr 0.11 2024-05-26 [2] RSPM (R 4.4.0)
## htmltools 0.5.8.1 2024-04-04 [2] RSPM (R 4.4.0)
## htmlwidgets 1.6.4 2023-12-06 [2] RSPM (R 4.4.0)
## httpuv 1.6.15 2024-03-26 [2] RSPM (R 4.4.0)
## httr 1.4.7 2023-08-15 [2] RSPM (R 4.4.0)
## IRanges * 2.38.1 2024-07-03 [1] Bioconductor 3.19 (R 4.4.1)
## jquerylib 0.1.4 2021-04-26 [2] RSPM (R 4.4.0)
## jsonlite 1.8.9 2024-09-20 [2] RSPM (R 4.4.0)
## knitr 1.48 2024-07-07 [2] RSPM (R 4.4.0)
## later 1.3.2 2023-12-06 [2] RSPM (R 4.4.0)
## lattice 0.22-6 2024-03-20 [3] CRAN (R 4.4.1)
## lifecycle 1.0.4 2023-11-07 [2] RSPM (R 4.4.0)
## magrittr 2.0.3 2022-03-30 [2] RSPM (R 4.4.0)
## Matrix 1.7-0 2024-04-26 [3] CRAN (R 4.4.1)
## MatrixGenerics * 1.16.0 2024-04-30 [1] Bioconductor 3.19 (R 4.4.1)
## matrixStats * 1.4.1 2024-09-08 [1] RSPM (R 4.4.0)
## memoise 2.0.1 2021-11-26 [2] RSPM (R 4.4.0)
## mime 0.12 2021-09-28 [2] RSPM (R 4.4.0)
## miniUI 0.1.1.1 2018-05-18 [2] RSPM (R 4.4.0)
## pillar 1.9.0 2023-03-22 [2] RSPM (R 4.4.0)
## pkgbuild 1.4.4 2024-03-17 [2] RSPM (R 4.4.0)
## pkgconfig 2.0.3 2019-09-22 [2] RSPM (R 4.4.0)
## pkgdown 2.1.1 2024-09-17 [2] RSPM (R 4.4.0)
## pkgload 1.4.0 2024-06-28 [2] RSPM (R 4.4.0)
## profvis 0.4.0 2024-09-20 [2] RSPM (R 4.4.0)
## promises 1.3.0 2024-04-05 [2] RSPM (R 4.4.0)
## purrr 1.0.2 2023-08-10 [2] RSPM (R 4.4.0)
## R6 2.5.1 2021-08-19 [2] RSPM (R 4.4.0)
## ragg 1.3.3 2024-09-11 [2] RSPM (R 4.4.0)
## Rcpp 1.0.13 2024-07-17 [2] RSPM (R 4.4.0)
## remotes 2.5.0.9000 2024-10-10 [1] Github (r-lib/remotes@5b7eb08)
## rlang 1.1.4 2024-06-04 [2] RSPM (R 4.4.0)
## rmarkdown 2.28 2024-08-17 [2] RSPM (R 4.4.0)
## S4Arrays 1.4.1 2024-05-20 [1] Bioconductor 3.19 (R 4.4.1)
## S4Vectors * 0.42.1 2024-07-03 [1] Bioconductor 3.19 (R 4.4.1)
## S7 0.1.1 2023-09-17 [1] RSPM (R 4.4.0)
## sass 0.4.9 2024-03-15 [2] RSPM (R 4.4.0)
## sessioninfo 1.2.2 2021-12-06 [2] RSPM (R 4.4.0)
## shiny 1.9.1 2024-08-01 [2] RSPM (R 4.4.0)
## SparseArray 1.4.8 2024-05-24 [1] Bioconductor 3.19 (R 4.4.1)
## SummarizedExperiment * 1.34.0 2024-05-01 [1] Bioconductor 3.19 (R 4.4.1)
## systemfonts 1.1.0 2024-05-15 [2] RSPM (R 4.4.0)
## textshaping 0.4.0 2024-05-24 [2] RSPM (R 4.4.0)
## tibble * 3.2.1 2023-03-20 [2] RSPM (R 4.4.0)
## tidyr 1.3.1 2024-01-24 [1] RSPM (R 4.4.0)
## tidyselect 1.2.1 2024-03-11 [1] RSPM (R 4.4.0)
## UCSC.utils 1.0.0 2024-04-30 [1] Bioconductor 3.19 (R 4.4.1)
## urlchecker 1.0.1 2021-11-30 [2] RSPM (R 4.4.0)
## usethis 3.0.0 2024-07-29 [2] RSPM (R 4.4.0)
## utf8 1.2.4 2023-10-22 [2] RSPM (R 4.4.0)
## vctrs 0.6.5 2023-12-01 [2] RSPM (R 4.4.0)
## withr 3.0.1 2024-07-31 [2] RSPM (R 4.4.0)
## xfun 0.48 2024-10-03 [2] RSPM (R 4.4.0)
## xtable 1.8-4 2019-04-21 [2] RSPM (R 4.4.0)
## XVector 0.44.0 2024-04-30 [1] Bioconductor 3.19 (R 4.4.1)
## yaml 2.3.10 2024-07-26 [2] RSPM (R 4.4.0)
## zlibbioc 1.50.0 2024-04-30 [1] Bioconductor 3.19 (R 4.4.1)
##
## [1] /__w/_temp/Library
## [2] /usr/local/lib/R/site-library
## [3] /usr/local/lib/R/library
##
## ──────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────